Motives behind acquiring an AI startup: analysis of notable transactions
This article was originally published on Medium, and scored 304 views.
More than 250 private AI (artificial intelligence) companies were acquired since 2012, according to CB Insights. Our research at Flint Capital left us with 340 companies.
Studying c.50 notable transactions (valuation of $50M and above) helps to define at least three approaches/rationales behind acquiring AI start-ups. The full article is on VentureBeat, some bullet points are below.
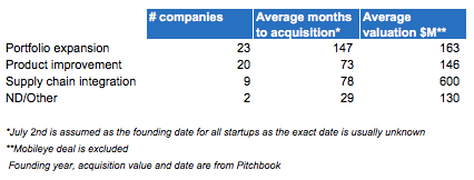
- Portfolio expansion is the most common rationale to acquire an AI startup. Seeking complementarity either across value chain (e.g. a company that offers cyber threats response acquires a threats detection specialist) or horizontal expansion (a NLP company acquires a startup that is exceptionally good with certain languages). E.g. Vertical: Splunk and Capsida. Horisontal: Nuance and SpeechMagic;
- Product improvement also takes place frequently, for example, when a diversified company acquires a specialist that has an edge over its existing offering. E.g. Bright.com and LinkedIn, Twitter and Magic Pony, Microsoft and Equivio;
- Supply chain integration, or transformative deals, are the least common type, and appear when industry-wide changes are expected, and a buyer tries to keep its assets and business relevant through acquiring players across the supply chain. E.g. Mako Surgical and Stryker, John Deere and Blue River Technologies, Google and DeepMind.
AI M&A transactions valued at $50M and above